Linux is a Unix-like operating system founded in the early 1990s by Finnish student Linus Torvalds and Free Software Foundation. While still a student at the University of Helsinki, Linus started to work on a personal project where he focused on ng up with Linux Kernel. On 17th September 1991 developed Version, 1.0 of Linux Kernel and the core of OS was estaestablished1994.
On the other hand, American software developer Richard Stallman in cooperation with FSF developed an open-source UNIX-like operating system called GNU. These utilities were then combined with Linux Kernel to create a complete system called GNU/Linux.
WHAT INSPIRED THE INVENTION OF LINUX?
The journey of Linux started around 1969 with Mainframe computers. This was when AT & T dropped from MULTICS.
In 1969, American Computer Science Legends Kenneth Lane Thompson and Dennis MacAlistair of AT & T Bell Labs created UNIX OS. The first version was out by 1970. The C programming language was created out of UNIX 2 years later to add portability and availability making UNIX more popular, highly adapted, modified, and copied by businesses and academic institutions across the globe.
In 1983, American developer Richard Mathew Stallman started a GNU project on creating a free UNIX-like operating system. There was sufficient software to build a complete operating system by the 1990s. The challenge still was that GNU Kernel was unable to pull enough development work rendering GNU incomplete.
In 1987, American-Dutch Professor Andrew S. Tanenbaum wrote an academic project on a UNIX-like system called MINIX. Source code was made available for everyone, but the system could not be modified or redistributed. This was 16-bits architecture-based and was not well suited to Intel’s increasingly popular 386 design for PCs. Therefore, it became expensive for private users to use UNIX for Intel 386 personal computers.
This prompted Linus Torvalds to start his new project on Linux Kernel.
The Linux System Architecture.
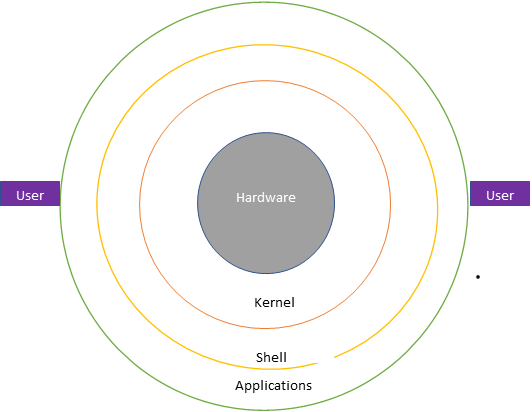
- Hardware: Consist of peripheral devices attached to the system e.g CPU, Disk RAM, etc.
- Kernel: This is a core component of OS that interacts directly with the hardware to provide low-level services to upper layer components.
- Shell: This is the interface between the user and the kernel. Takes instructions or commands from user or application the sends to Kernerl. Also picks processed data from kernel to application or user.
- Applications: These are utility programs that run on the shell.
Linux Systems File Systems.
- Ext: Was primarily developed for MINIX OS.
- Ext2: First Linux FS that allows 2TB.
- Ext3: Upgraded version of Ext2. Does not support servers because it does not support disk recovery and snapshots.
- Ext4: Default FS in Linux systems. Fasted among Ext file systems and very compatible with SSD disks.
- JFS: Journaled File System was developed by IBM for AIX Unix as an alternative to Ext files.
- ReiserFS File System: Natively preferred as SUSE file system but due to changes in some policies SUSE returned to Ext3. It dynamically supports the file extension but has some drawbacks in performance.
- XFS: This is considered a high-speed JFS that was developed for parallel I/O processing.
- Btrfs; This Is a good suit for the production file systems. Is used for fault tolerance, repair systems, fun administration, extensive storage configuration, etc.
- Swap: Used for memory paging during hibernation.
Linux Distributions.
Linux distribution is an operating system developed from software comprising of Linux kernel. This can be subdivided into two major groups:
RHEL-based systems which include Rocky, CentOS, Oracle, Fedora, CearOS, etc.
Debian-based systems: Debian, Ubuntu, Mint, Zorin, Kali, Parrot, etc.

Advantages of Linux.
- Highly Secure
- Stable
- Free and Open Source
- Easy to use
- Absolute Freedom over your system
- High Performance
- Proper use of System Resources
- Privacy-Friendly
- Easily Install Software
- Better Software Updates
Disadvantages of Linux
- No standard edition
- Hard Learning Curve
- Limited market share
- Lack of proprietary software
- Difficult to troubleshoot
- Poor support for games
- Unsupported Hardware
- Lack of technical support